 Increasing Efficiency and Reducing Administrative Burden in Managing Injuries
Increasing Efficiency and Reducing Administrative Burden in Managing Injuries
By Isaac Smith, Editorial Director, Hong Kong Sports Clinic
LinkedIn: Isaac Smith
LinkedIn: Hong Kong Sports Clinic
Injury care management requires precision, efficiency, and streamlined processes to treat patients quickly and effectively. Health Information Technology (Health IT) solutions have transformed injury management workflows, efficiency, and administrative burdens as healthcare systems evolve. This article discusses how Health IT solutions can transform injury care, including their benefits, implementation strategies, and future trends.
Health IT technologies store, share, and analyze health data. EHRs, telemedicine platforms, and HIEs are examples. These technologies help healthcare providers streamline operations, improve patient care, and reduce administrative time.
What is the Administrative Burden in Healthcare?
Administrative burden is the time and effort physicians, health care providers, clinicians, and administrative staff spend on administrative clinical support functions separate from patient care.
Examples of such tasks may include:
- Required patient visit and treatment plan documentation
- Handling complicated health insurance claims and disputes
- Managing patient referrals to specialists or other healthcare facilities
- Coordinating care between multiple providers, which requires a lot of paperwork and communication
- Managing medication refills and prior authorizations
- Updating coding and billing regulations requires ongoing education and training.
- These tasks are necessary for healthcare practices, but they can take up a lot of time, reducing patient care.
Administrative waste in healthcare is wasteful administrative spending that does not improve patient care or outcomes.
Considerations For Advancing Health Care Workflow Automation
Workflow efficiency is a major benefit of Health IT in injury care. EHR systems enable healthcare providers to seamlessly share patient data. This makes all medical history, diagnostic results, and treatment plans available in real time, enabling faster and more accurate decision-making.
Automation and reminders for follow-up appointments are also important in Health IT. These systems reduce appointment misses and ensure prompt care. Integration of diagnostic tools and imaging systems into Health IT platforms speeds analysis and diagnosis, improving injury care efficiency.
The key informant interviews, literature review, and workshop revealed workflow automation barriers and facilitators that health care automation must address. These considerations can help health care stakeholders—patients, caregivers, clinicians, staff, technology developers, researchers, provider organizations, payors, policymakers, and accrediting bodies—address the many design, implementation, and use factors of automating workflows.
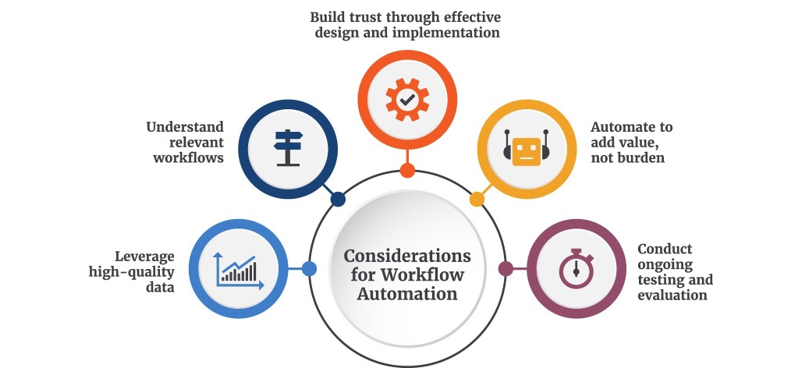
Leverage high-quality data
When automating health care workflows, high-quality data is crucial. Patient, caregiver, clinician, and staff experience, safety, and outcomes can be affected by automation data quality. Automation solutions may use administrative, cost, frequency, duration, clinical, and outcome data and metadata.
Data limitations must be understood to avoid completeness, consistency, reliability, and accuracy issues. Use of industry consensus standards may improve automation data quality. When used with evidence-based workflows, such standards can reduce ad hoc mapping, improve automation reliability and repeatability, and enable automation approach reuse.
Understand relevant workflows
Change comes from automation. Automation will change how one task or a health care workflow is done. Understanding the workflow and goals is crucial to developing and measuring automation solutions. The proposed automation solution must consider the workflow’s tasks, technology, organization, context, and people.
Build trust through effective design and implementation
Stakeholder buy-in and trust are crucial to automation solution design and implementation. For workflow automation solutions to be implemented, adopted, and used, patients, caregivers, clinicians, and staff must be invested in the change. Identification of automation needs and benefits requires a robust, systematic process with fully engaged stakeholders, including direct users (e.g., patients or clinicians) and others impacted by a workflow (e.g., organizational leadership).
Establishing clear, common goals and explaining what automation will improve, how it will work, and what it will not replace requires clear communication. Poor communication and user experiences, including poor training, can quickly erode trust because frustration and decreased enthusiasm for change obscure automation’s intended benefits. This is why health care workflow automation solutions must be accurate, reliable, and not increase patient safety risks.
Automate to add value, not burden
A commitment to high-quality, equitable care should drive health care workflow automation success. When automating health care workflows, consider whether it will add value, safety, or efficiency. This includes ensuring automation serves all patient populations without biasing or favoring one. Adding automation to a health care workflow often allows for a complete workflow redesign to support automation.
Conduct ongoing testing and evaluation
Testing and evaluation will be crucial before, during, and after implementation. Automation projects need feedback loops to monitor the technology and its effects. This should help assess whether the automation is working, measuring its impact, and meeting automation goals. Automation must improve one or more health care delivery ecosystem dimensions and be measured.
The above considerations can help advance health care workflow automation along with clear priorities and relevant strategies.
Reducing Administrative Burden
Health IT solutions also reduce administrative burdens on healthcare providers and staff:
Simplifying Billing and Coding Processes:
The process of generating and submitting insurance claims is streamlined by automated billing systems, which also reduces the number of errors that occur and ensures that reimbursement occurs more quickly. In addition, health information technology solutions can be of assistance in accurately coding procedures, which is an essential component of injury care documentation.
Automating Insurance Claims and Authorization Management:
The verification of insurance coverage and the acquisition of pre-authorization for procedures can be automated through the use of health information technology solutions, which will reduce the amount of time and effort that administrative staff must expend.
Reducing Paperwork and Manual Data Entry:
The elimination of the need for extensive paperwork and manual data entry is made possible by digital records, which enables administrative staff to concentrate on more important tasks. Not only does this improve efficiency, but it also lessens the likelihood of errors that are associated with the processes of manually handling data.
Enhancing Communication:
Health information technology solutions make it possible for patients, insurance companies, and healthcare providers to communicate with one another in a seamless manner. The use of secure messaging systems and patient portals enables the sharing of information, the scheduling of appointments, and the latest updates on treatment plans, which ultimately leads to an improvement in overall coordination and patient satisfaction.
Conclusion
Health IT is improving efficiency and reducing administrative burdens in injury care management. EHRs, telemedicine platforms, and HIEs help healthcare providers streamline operations, improve patient care, and focus more on direct patient interactions than administrative tasks.
By simplifying billing and coding, automating insurance claims and authorization management, reducing paperwork, and improving patient, provider, and insurer communication, health IT solutions reduce administrative burden. These improvements speed up and improve decision-making, care coordination, and patient outcomes.
Successful Health IT implementation requires workflow knowledge, high-quality data, stakeholder trust, and ongoing testing and evaluation. Focusing on these areas helps healthcare organizations ensure automation adds value without adding burdens or risks.
Health IT will likely play a larger role in injury care management as healthcare evolves, driving patient care innovations and efficiencies. Healthcare providers must adopt these technologies to stay competitive and meet growing demands.
